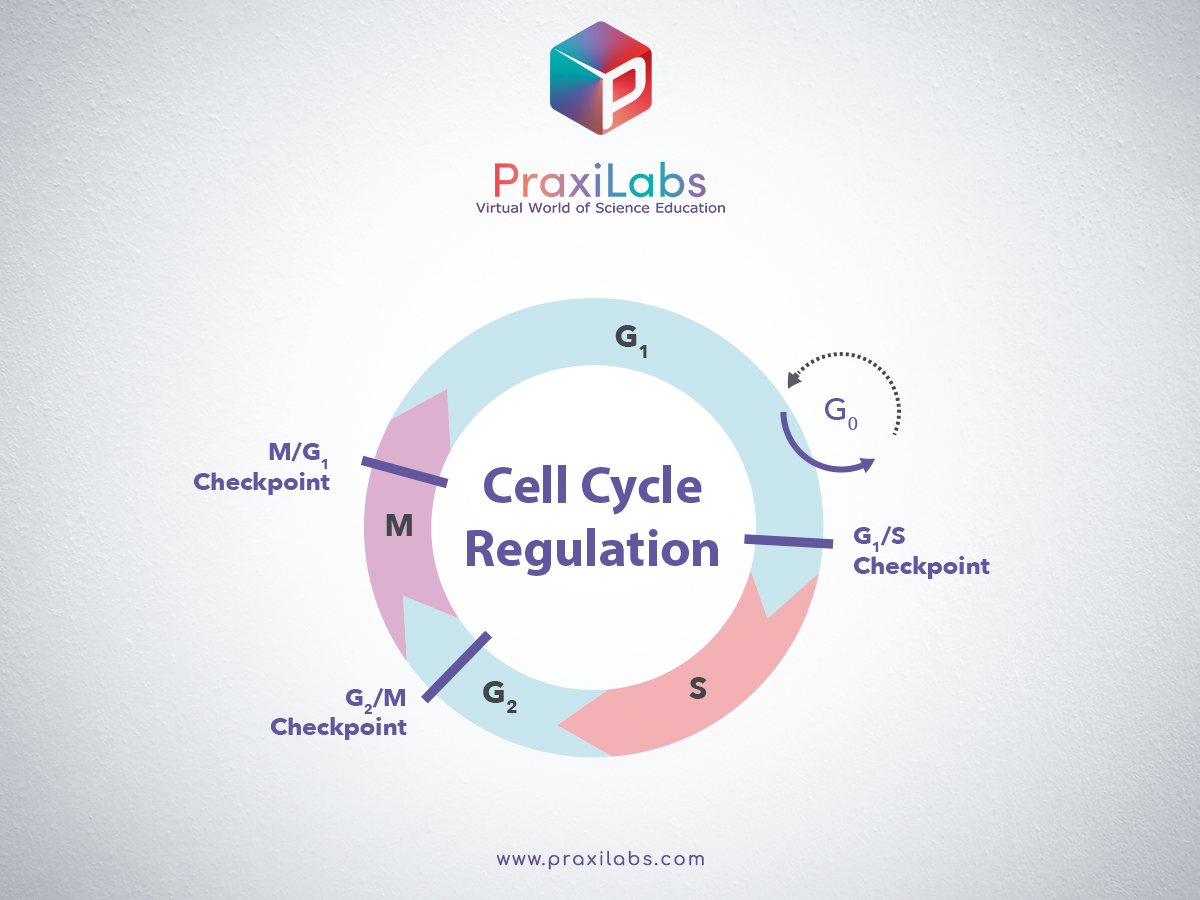
Cell Cycle Regulation Cyclins and CDKs Biology Diagrams Read More: Mitosis- definition, purpose, stages, applications with diagram 6. Cytokinesis. Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm into two halves, indicating the end of cell division. checkpoint prevents the entry of cells into the S phase of the cycle by preventing the activation of regulators like cyclins and CDKs.
Download scientific diagram | The cell cycle and its regulation by cyclins, CDKs, and CDKIs. The cell cycle is divided into four distinct phases (G 1 , S, G 2 , and M). The progression of a cell • CDKs are always present, so rather than getting rid of them, must get rid of CDK activity - regulate activity • => CDKs need to be activated: • Without cyclins, CDK active site is blocked by a portion of its own amino acid sequence • Cyclin binding partially exposes the active site by causing a conformation change • To be fully active, CDKs need an activating P(phosphate

Cell Cycle Regulation: Cyclins and CDKs Biology Diagrams
Cyclins Determine the Activity of CDKs (named because their levels change during the cell cycle). Cyclins are divided into four classes defined by their presence and activity during the cell cycle: G1 Cyclins (D cyclins) G1/S cyclin (Cyclin E) S-phase cyclins (cyclins E and A) M-phase cyclins (B cyclins) G1 cyclins (Cyclin D) coordinates the The cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), CDK inhibitors (CKIs), and checkpoint proteins are examples of these internal signals that keep an eye on cellular parameters like cell growth, chromosome alignment, and DNA integrity. Protein kinases are the enzymes that activate or inactivate other proteins. They do these by phosphorylation.

Download scientific diagram | 9: Overview of the CDKs and the cyclins. Each cyclin binds to one or several CDKs, which phosphorylate several different substrates. Cyclin-CDKs regulate

The cell cycle phases and their associated cyclin Biology Diagrams
Cyclins and CDKs as in charge molecules of cell cycle progression, therefore their negative regulator actions are in focus in many cancer mechanism (García-Reyes et al., 2018). CDKs having role Cell cycle regulation. At the end of mitotic metaphase: cyclin B level degradation begins resulting in lower amount of active MPF which brings about anaphase, telophase cytokinesis and eventually the cells reenters interphase.In summary, High levels of active MPF stimulate G2/M progression or mitosis whereas low levels favour return to interphase.DNA damage is the major reason that prevents
